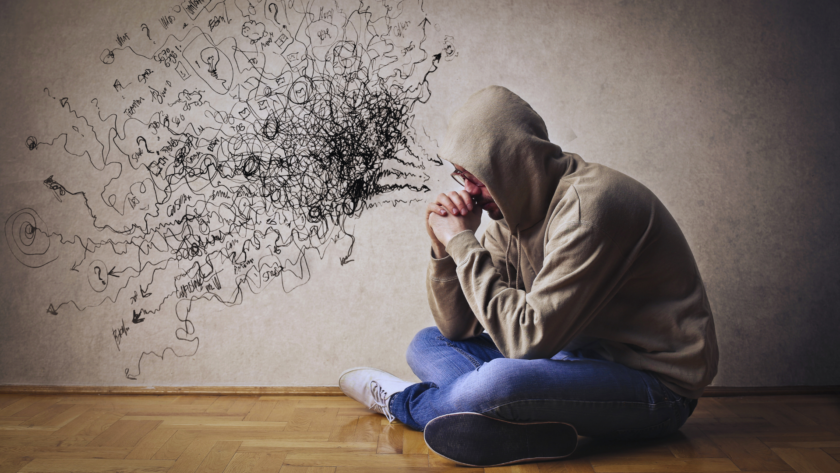
Negative self-talk can significantly impact mental health, leading to feelings of inadequacy and stress. Recognizing and addressing this internal dialogue is essential for fostering a more positive mindset. Simple strategies can empower individuals to reframe their thoughts and reduce the influence of negativity.
Awareness is the first step in combating negative self-talk. By identifying harmful patterns, they can begin to challenge these thoughts and replace them with more constructive alternatives. Techniques such as mindfulness, journaling, or cognitive restructuring can help shift focus from self-criticism to self-acceptance.
Engaging in supportive self-talk is crucial for emotional well-being. When individuals consciously replace negative statements with affirmations or realistic assessments, they create a healthier internal dialogue. This shift not only improves mental health but also enhances overall quality of life.
Understanding Negative Self-Talk
Negative self-talk is often characterized by a consistent pattern of critical and self-defeating thoughts. Identifying its triggers and understanding its effects are fundamental for mental and emotional well-being.
Identifying Triggers and Patterns of Negative Self-Talk
Triggers for negative self-talk can vary greatly among individuals. Common triggers include stressful situations, failure, or comparisons with others. Recognizing these triggers allows for proactive strategies to manage thoughts before they spiral.
Patterns of negative self-talk may manifest as self-criticism, where individuals harshly judge their actions or choices. Other patterns include catastrophizing, where minor setbacks are blown out of proportion. Keeping a journal can help track these thoughts and identify recurring themes that affect mental and emotional health.
Effects of Negative Self-Talk on Mental and Physical Health
Negative self-talk can lead to significant consequences for both mental and physical health. Research shows that it is closely linked to conditions like anxiety and depression. Persistent negative thoughts can create a cycle of low self-esteem and increased stress.
Physically, negative self-talk may contribute to symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and changes in appetite. Stress hormones released during episodes of negative thinking can impact the immune system and overall well-being. Understanding these effects underscores the importance of addressing negative self-talk effectively.
Strategies for Overcoming Negative Self-Talk
Negative self-talk can hinder personal growth and impact self-esteem. Effective strategies can foster a healthier mindset and improve overall mental well-being. The following methods offer practical approaches to combat negative thoughts.
Adopting a Mindfulness Approach
Mindfulness involves being present and fully engaged in the moment. This practice can help individuals recognize and detach from negative self-talk without judgment.
To adopt mindfulness, one can:
- Practice meditation: Even a few minutes daily can enhance awareness.
- Use breathing techniques: Focused breathing promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.
- Engage in mindful activities: Simple tasks, like eating or walking, can heighten awareness of thoughts.
These practices encourage self-compassion and help individuals view their thoughts as temporary rather than absolute truths. Recognizing patterns can pave the way for more positive internal dialogue.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) equips individuals with tools to challenge and reframe negative thoughts. It emphasizes understanding thought patterns and replacing harmful beliefs with realistic standards.
Key techniques include:
- Identifying cognitive distortions: Recognizing patterns, such as all-or-nothing thinking, helps to intervene before negative thoughts escalate.
- Journaling: Writing down thoughts allows individuals to analyze them critically and track progress over time.
- Setting specific goals: Achieving small, manageable objectives promotes motivation and reinforces positive self-talk.
CBT can be beneficial for those seeking professional help. These techniques foster a shift in perspective, enhancing self-esteem.
Developing Positive Self-Talk Habits
Cultivating positive self-talk is essential for maintaining mental health. It involves consciously replacing negative thoughts with affirming statements.
Actionable strategies include:
- Using positive affirmations: Reciting affirmations daily reinforces self-worth and confidence.
- Gratitude practices: Regularly reflecting on positive aspects of life can shift focus away from negativity.
- Surrounding oneself with positivity: Engaging with supportive people encourages a healthier mindset.
By developing these habits, individuals can create a more encouraging internal dialogue, contributing to personal growth and resilience against mental disorders.
Lifestyle Choices Supporting Mental Health
Making conscious lifestyle choices can significantly enhance emotional well-being and reduce negative self-talk. Key elements include sleep quality, diet, relationships, and regular physical activity.
Importance of Sleep and Healthy Diet
Quality sleep is crucial for mental health. It helps regulate mood and reduces stress. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. A consistent sleep schedule enhances sleep quality.
A balanced diet rich in nutrients also supports mental health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish and nuts, can improve mood. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential vitamins and minerals. Staying hydrated is equally important; drinking enough water can help maintain energy levels and focus.
Fostering Healthy Relationships
Strong, positive relationships contribute significantly to emotional well-being. Surrounding oneself with supportive individuals can provide a buffer against negative thoughts. Good communication fosters trust and understanding.
Engaging in activities with friends or family can enhance feelings of belonging and support. Practicing gratitude by noting positive interactions can deepen connections. Consider keeping a gratitude journal to reflect on these moments regularly. Building and maintaining these relationships plays a critical role in overall mental health.
Physical Activity and Mental Health
Regular physical activity has profound effects on mental health. It promotes the release of endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
Activities like walking, swimming, or dancing can be enjoyable ways to stay active. Even simple exercises, such as stretching, can alleviate anxiety. Consistent physical activity supports not only physical health but also enhances self-esteem and emotional resilience.