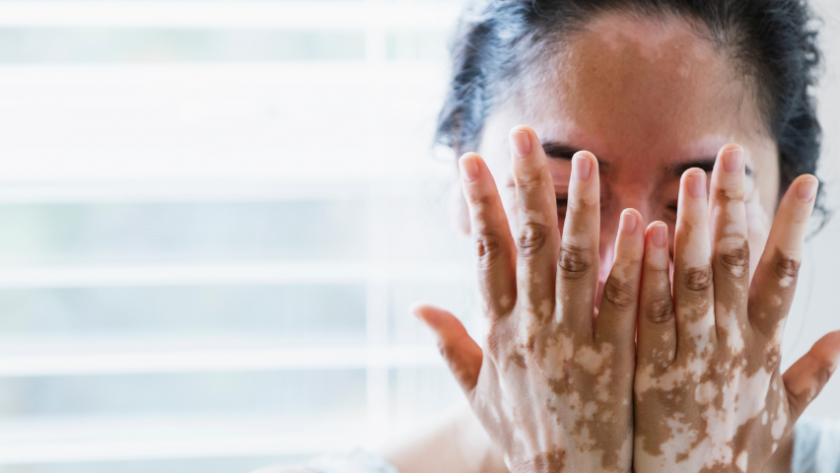
Vitiligo is a disease with an unknown cause and no known cure. It affects both sexes and is found in people of all ethnic backgrounds.
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a skin condition that causes white patches to appear on the skin. It is usually a harmless condition, but there is a small risk that the patches may become infected, and it can also cause skin fragility, so it should be treated by a skin specialist.
It is a skin disease that affects the skin and is characterized by loss of skin pigment in patches. It is most often caused by a loss of pigment in the skin and is often accompanied by a loss of pigment in other organs, such as the eyes, hair, and internal organs.
Vitiligo is a skin disorder that causes patches of the skin to lose the pigment melanin, either as a result of damage or as a response to an immune response.
There are two types of vitiligo, the common type, and the rarer, congenital type. The common form of vitiligo affects people of all racial and ethnic groups and is caused by several triggers. The rarer form, which is inherited and presents as a childhood disorder, is less common and usually affects people of African-American descent.
Causes
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder that causes the loss of skin pigment (melanin). The most common type is acquired (partial) vitiligo, in which patches of depigmented skin appear on the face and limbs. A less common form is congenital (generalized) vitiligo, in which the entire body is affected. Vitiligo is caused by an autoimmune response to melanocytes in the skin, and it is more common in people with atopy (a family history of allergic disease) or people with high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Vitiligo is a condition in which the pigment-producing cells in the skin are destroyed, leading to loss of pigmentation in the affected area. It is the most common pigment-related disorder in the world.
The first stage of vitiligo is the first visible change, where the first signs of the condition are visible-the skin color changes, which are followed by the development of splotches. Like the skin color changes, the vitiligo usually starts at the edges of the skin first, then develops into the middle portion of the skin, then the whole skin.
Vitiligo Symptoms
Everyone is different. Some people have a lot of pigment in their skin. Some have a little. Some people have a lot of pigment in their skin. Some have a little. But, whatever the case may be, many people deal with something called Vellus Hair Loss. Vellus Hair Loss, or Vitiligo, is a skin disorder that can cause a loss of pigment in the skin.
The disease is usually more prevalent at the top of the body but can affect all of the skin. The areas most affected are the face, hands, arms, legs, feet, and genitalia. It is not contagious but can be very disfiguring.
Best Vitiligo Treatment
Many people who have vitiligo have a lot of questions about what treatments can help their condition. There are a lot of different treatments that have been proven to help vitiligo, but there are also a lot that has not been proven to help vitiligo. While many treatments have not been proven, there are a few that have been proven to help with vitiligo. Patients can choose from a variety of treatments, including: – Hydroquinone creams – Hydroquinone pills – Topical creams – Topical pills – Vitiligo injections.
If you’ve been diagnosed with vitiligo, you can look forward to a lifetime of visits to dermatologists and possibly even costly treatments. There might be light at the end of the tunnel with medical therapies such as laser therapy and injections, but these can come with their share of side effects and recovery time.
Vitiligo is a common skin disorder that causes loss of skin pigmentation. It affects an estimated 6% of the population and is usually lifelong. The exact cause of the disorder is unknown, but the disorder is not contagious or hereditary. It is considered to be a cutaneous disorder, which means that there are no associated structural changes.
The condition is classed as an autoimmune disease, where the body’s immune system attacks healthy skin cells, leaving behind patches of skin that are lighter than the rest of the skin.